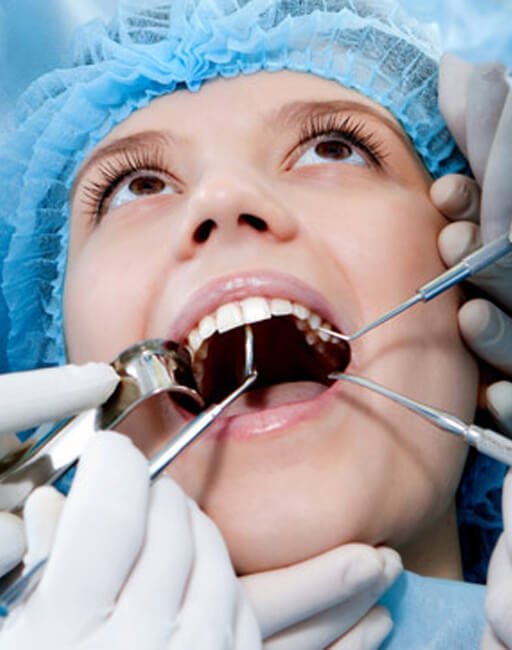
Why is Oral Surgery Conducted?
You could require oral surgery for dental treatments outside a conventional dentist’s scope. For instance, you may need to consult an oral surgeon for wisdom tooth extraction. Likewise, you may have to visit a periodontist if you have gum disease and require a gum transplant.
Your regular dentist will discuss the procedure and direct you to the appropriate specialist for further treatment.
How is oral surgery performed?
Dental surgeons create incisions along your gum line during this procedure and pull back the tissue from your teeth. They will then flush away the plaque and bacteria that have built up on your gums when they clean the roots of your teeth. The gum tissue is finally replaced and secured in place using sutures.
Tooth extraction is the most typical oral surgery procedure (tooth removal).
Your dentist will advise extraction if you have gum disease (periodontitis), severe tooth decay, issues with your wisdom teeth, or dental trauma. Removing some of your teeth may be necessary to prepare your mouth for prosthetic devices such as dentures.
Often periodontists and oral surgeons perform a tooth extraction.